Tenomerga
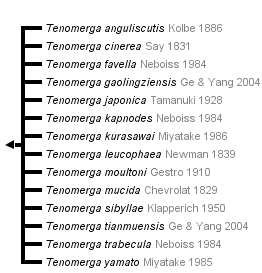

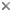
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
With 14 extant species (see table), the genus Tenomerga is the largest among Cupedidae and Archostemata in general. Species of this genus are found in North America (T. cinerea) and South Africa (T. leucophaea) but most species occur in the south-east Asiatic area.
The species of Tenomerga are characterised by short, compact heads with usually distinct posterior dorsal head tubercles. The different species can grow in total length from 7mm up to ca. 20mm.
Currently known species of Tenomerga
| Tenomerga | Junior synonyms | Distribution | Total length, ca. [mm] | Total width, ca. [mm] | Length/width ratio, ca. | Larvae |
| anguliscutis (Kolbe, 1886) | Cupes anguliscutis Kolbe, 1886 Cupes formosanus Tamanuki, 1928 | Korea; Vietnam; Laos; eastern China (Mandshuria); Taiwan | 10 to 12.4 | 2.7 to 3.6 | 3.7 | unkown |
| cinerea (Say, 1831) | Cupes cinereus Say, 1831 Cupes concolor Westwood, 1835 Cupes trilineatus Melsheimer, 1845 Cupes oculatus Casey, 1897 | eastern North America (USA; Canada) | 7.5 to 14 | 1.7 to 3.6 | 4 | one instar and pupa studied by Snyder (1913) and Grebennikov (2004), larvae live in wood of broad-leafed plants infested by the fungus Daedalea quercina (Snyder 1913, 1956) |
| favella Neboiss, 1984 | Borneo | 9.7 | 2.1 | 4.6 | unknown | |
| gaolingziensis Ge & Yang, 2004 | eastern China | 10.8 | 2.1 | 5.1 | unknown | |
| japonica (Tamanuki, 1928) | Cupes japonicus Tamanuki, 1928 | Japan, Honshu; possibly also in China (ref. Vulcano & Pereira 1975 and specimen in collection of BMNH) | 9 to 14 | 2.3 to 3.9 | 3.7 | unknown |
| kapnodes Neboiss, 1984 | eastern part of New Guinea | 8 to 9 | 2 to 2.3 | 4 | unknown | |
| kurosawai Miyatake, 1986 | Japan, probably endemic on the island of Yaku-shima, near the southern coast of Kyushu | 12.5 to 15 | 3.2 to 4 | 3.8 | unknown | |
| leucophaea (Newman, 1839) | Cupes leucophaea Newman, 1839 Cupes capensis Kolbe, 1897 | South Africa (southern and south-eastern coasts) | 15.7 to 20 | 4 to 4.6 | 4 | unknown |
| moultoni (Gestro, 1910) | Cupes moultoni Gestro, 1910 | Borneo; Philippines (Mindanao) | 7 to 9.7 | 2 to 2.3 | 4.1 | unknown |
| mucida (Chevrolat, 1829) | Cupes mucidus Chevrolat, 1829
| Japan, eastern coasts of Russia (south-east Siberia) to southern coasts of China; Phillipines; Hawaii (probably introduced) | 10 to 14.5 | 2.8 to 4.5 | 3.6 | two instars & pupa studied by Fukuda (1938, 1939, 1941) and Grebennikov (2004) |
| sibyllae (Klapperich, 1950) | Cupes sibyllae Klapperich, 1950 | south-east China | 10.9 to 12.4 | 2.9 to 3.4 | 3.6 | unknown |
| tianmuensis Ge & Yang, 2004 | eastern China | 12.3 | 2.8 | 4.4 | unknown | |
| trabecula Neboiss, 1984 | eastern China; Taiwan | 10 to 13.2 | 2.5 to 3.4 | 4 | unknown | |
| yamato Miyatake, 1985 | Japan, Kyushu | 9.5 to 11 | 2.4 to 2.8 | 3.8 | unknown |
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
The phylogenetic relationships of the species of Tenomerga were analysed by Hörnschemeyer (2009). An interesting result of this analysis is the postulation of a close relationship of T. leucophaea with Cupes capitatus and Rhipsideigma, rendering Tenomerga in ist current designation non-monophyletic. Such a relationship becomes plausible when Tenomerga fossils from Europe are taken into account. Motschulsky 1856, Peyerimhoff 1909, Gersdorf 1976, Tröster 1993, Wedmann 200 and Wappler 2003 described compression and amber fossils of Eocene to Pleistocene age from Europe that closely resemble C. capitatus as well as T. leucophaea in their character composition.
Otherwise the species of Tenomerga are grouped in two clades, one comprising the North American T. cinerea and the eastern Asiatic species (see cladogram), the second clade contains T. favella, T. kapnodes and T. moultoni.
References
Casey, T. L. 1897. Coleopterological notices VII, Cupesidae. - Annals of the New York Academy of Science 9: 637-638.
Chevrolat, A. 1829. Iconographie du Règne Animal - In: Guérin-Méneville, F. E.: Iconographie du Règne Animal, Vol. 3: 58.
Ge, S.-Q. and X.-K. Yang. 2004. Two new Chinese species of Tenomerga Neboiss (Coleoptera: Cupedidae), with a world catalog of the genus. Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington 106(3):631-638.
Gersdorf, E. 1976. Dritter Beitrag über Käfer (Coleoptera) aus dem Jungtertiär von Willershausen, Bl. Northeim 4226. - Geologisches Jahrbuch A 36: 103-145.
Gestro, R. 1910. Contribuzione allo studio dei Cupedidi. - Annali del Museo civico di storia naturale di Genova 4: 454-456.
Klapperich, J. 1950. Eine neue Art der Cupesidae (Coleoptera) aus Asien. - Bonner Zoologische Beiträge Heft 1: 83-85.
Kolbe, H. J. 1886. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Coleopteren-Fauna Koreas. - Archiv für Naturgeschichte 52: 139-240.
Melsheimer, F. E. 1845. Descriptions of new species of Coleoptera of the United States. - Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 2 (12): 302-318.
Miyatake, M. 1986. A new species of the genus Tenomerga (Coleoptera, Cupedidae) from Yakushima Island, southwest Japan. - In: Ueno, S.I. (Ed.). Entomological papers presented to Yoshihiko Kurosawa on the occasion of his retirement. Coleopterists‘ Association of Japan, Tokyo: 111-114.
Neboiss, A. 1984. Reclassification of Cupes Fabricius (s.lat.), with descriptions of new genera and species (Cupedidae: Coleoptera). Systematic Entomology 9: 443-477.
Newman, E. 1839. XXXV.-Supplementary note to the synonymy of Passandra. - Annals and Magazine of Natural History (Zoology, Botany, and Geology) 3 (18. 303 - 305.
Pascoe, F. P. 1872. Notes on Coleoptera, with descriptions of new genera and species. Part 2. - Annals and Magazine of Natural History (4) 10: 317-326.
Say, T. 1835. Descriptions of new North American coleopterous insects, and observations on some already described. - Boston Journal of Natural History Vol. I (1834-1837): 151-202.
Solsky, S. 1871. Coleoptères de la Siberia orientale. - Horae Societatis Entomologicae Rossicae 7 (1870): 334-406.
Tamanuki, K. 1928. A taxonomic study of the Japanese Cupedidae. - Zoological Magazine, Tokyo 40: 242-254.
Tröster, G. 1993. Two new Middle European species of the genus Tenomerga Neboiss 1983 from the Middle Eocene of Grube Messel and the Eckfelder Maar (Coleoptera: Archostemmata[sic]:Cupedidae). Mainzer naturwiss. Archiv. 31:S169-176.
Wedmann, S. 2000. Die Insekten der oberoligozänen Fossillagerstätte Enspel (Westerwald, Deutschland). - Mainzer naturwissenschaftliches Archiv Beiheft 23: 1-154.
Westwood, J. O. 1835. Insectorum Arachnoidumque novorum Decades duo. - The Zoological Journal 5 (20. 440-453.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Tenomerga cinerea |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| View | Dorsal |
| Image Use |
 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1996 David R. Maddison

|
About This Page
Page copyright © 2011
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 10 February 2006
- Content changed 22 November 2011
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 2011. Tenomerga . Version 22 November 2011 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Tenomerga/9009/2011.11.22 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/










 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site